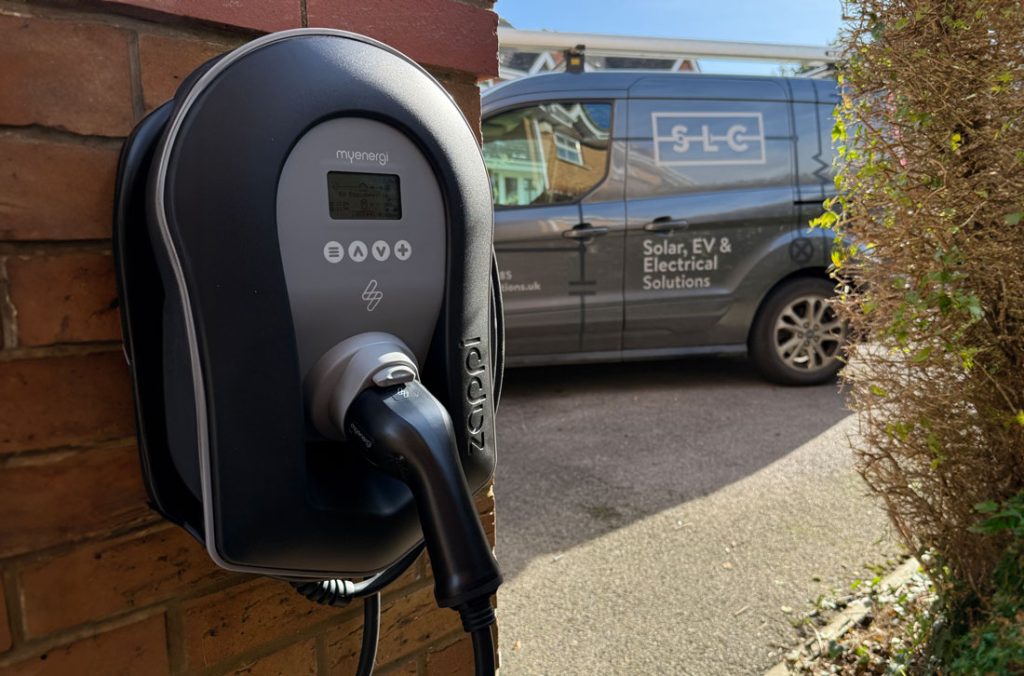
With the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and the shift toward sustainable energy, more people are investing in EV chargers for their homes and businesses. But with various options available on the market, selecting the right EV charger for your needs can seem overwhelming. This guide will break down the key factors you need to consider when choosing the best EV charger for your specific situation, whether you’re looking for a home charger or a commercial solution.
1. Understanding EV Charger Types
Before diving into the selection process, it’s essential to understand the types of EV chargers available. There are three main levels:
Level 1 Chargers (120V)
- Speed: The slowest charging option.
- Installation: Can be plugged into a standard 120V outlet without professional installation.
- Use Case: Ideal for occasional EV owners who drive short distances daily and have access to an outlet overnight.
- Charging Time: Can take 8-12 hours to charge an EV fully.
Level 2 Chargers (240V)
- Speed: Much faster than Level 1 chargers.
- Installation: Requires professional installation of a 240V outlet (similar to a clothes dryer or oven).
- Use Case: Best for regular EV users or anyone who needs to charge their car faster.
- Charging Time: Typically takes 4-6 hours to fully charge an EV, depending on the vehicle and charger.
DC Fast Chargers (DCFC)
- Speed: The fastest charging option.
- Installation: Requires specialized infrastructure, often only available at public charging stations.
- Use Case: Mostly used by businesses, fleets, or commercial charging stations for quick, high-volume charging.
- Charging Time: Can charge an EV to 80% in 30 minutes.
For most residential users, a Level 2 charger is the most practical option, offering a balance of speed and convenience.
2. Charging Speed: How Fast Do You Need to Charge?
The speed at which you charge depends on how often and how far you drive, as well as how much time you have available to charge your vehicle.
- If you’re a daily commuter: If you drive moderate distances (30-50 miles a day), a Level 2 charger is probably the best option. It ensures you have enough charge overnight, even if you drive the car every day.
- If you’re a weekend driver or rarely drive long distances: A Level 1 charger might be sufficient, especially if you don’t mind charging overnight.
- If you have multiple EVs or run a fleet: A DC Fast Charger is ideal for businesses or properties that need to keep vehicles charged quickly and efficiently.
It’s crucial to match the charger’s speed with your driving habits and charging needs. For most households, a Level 2 charger offers the best balance between cost, convenience, and speed.
3. Power Output and Charging Capacity
Each EV charger has a specific power output, typically measured in kilowatts (kW). The higher the kW, the faster the vehicle will charge. For example, most Level 2 chargers have a power output of around 7 kW to 22 kW.
When selecting a charger, ensure your home’s electrical system can handle the power output of the charger. In some cases, a home’s electrical panel might need an upgrade to support a higher output charger.
It’s also essential to check the vehicle’s onboard charger capacity. Even if you install a charger with a higher output, the car will only charge at the maximum rate it can accept. So, choosing a charger that matches both your vehicle’s and your home’s capacity ensures efficiency.
4. Smart Features: Adding Convenience and Control
Modern EV chargers often come with smart features that allow you to monitor, schedule, and control your charging remotely. These features can add convenience, energy savings, and insights into your charging habits. Some smart chargers include:
- App Control: Monitor charging status, start or stop charging remotely, and track energy consumption via an app.
- Scheduling: Set specific charging times to take advantage of off-peak electricity rates.
- Energy Monitoring: Track how much energy your EV uses and estimate costs.
- Remote Diagnostics: Get alerts and troubleshoot potential issues remotely.
Smart chargers can be particularly beneficial for households with multiple EVs or businesses that need to manage charging times and costs efficiently.
5. Installation Considerations
The installation process for an EV charger can vary depending on the type of charger and your home’s electrical system. A Level 1 charger typically requires no installation beyond a standard 120V outlet. However, for a Level 2 charger, professional installation is needed to ensure the system is safely connected to your home’s electrical supply.
Here are some installation considerations:
- Location: Choose a location near your EV parking space, ensuring the charger’s cable can reach the vehicle.
- Electrical Panel: Ensure your electrical panel can handle the additional load. For higher-power chargers, you may need an electrical panel upgrade.
- Permitting: Some regions require permits for electrical installations, so check local regulations before proceeding.
It’s crucial to hire a licensed electrician for the installation to ensure safety and compliance with local codes.
6. Cost: What’s Your Budget?
The cost of EV chargers can vary widely, from a few hundred dollars for a basic Level 1 charger to several thousand dollars for high-end, feature-rich Level 2 chargers. Installation costs are an additional expense, and prices will vary depending on the complexity of the installation.
Here are some price estimates:
- Level 1 Charger: $200 – $500 (excluding installation)
- Level 2 Charger: $500 – $2,000 (excluding installation)
- Installation: $300 – $2,000, depending on the complexity of the electrical work
Consider both the upfront cost and long-term savings when selecting a charger. A Level 2 charger will likely offer the best value for regular EV users, with quicker charging times that can improve daily convenience.
7. Vehicle Compatibility
Ensure the charger you select is compatible with your specific EV model. Most EVs use a standard connector, known as the J1772 connector for Level 1 and Level 2 chargers. However, certain manufacturers like Tesla use a proprietary connector. If you drive a Tesla, you may need an adapter or a Tesla-specific charger.
Double-check your vehicle’s charging port and compare it with the charger’s connector type to ensure compatibility.
8. Environmental Considerations
As EV adoption grows, choosing a charger with a smaller carbon footprint is an essential consideration. Many manufacturers now offer chargers made from sustainable materials or designed to minimize energy consumption. Additionally, pairing your EV charger with a solar power system can reduce your environmental impact even further.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Needs
Selecting the right EV charger depends on various factors such as charging speed, power output, smart features, installation requirements, and cost. By considering your driving habits, home’s electrical capacity, and future needs, you can make an informed decision that ensures convenience, efficiency, and long-term savings.
At SLC Solutions, we specialize in providing expert advice and professional installation of EV chargers, tailored to your needs. Whether you’re looking to install a charger for your home or business, we can guide you through the process and ensure you get the right solution for your electric vehicle.
If you’re ready to switch to electric or upgrade your current charging setup, reach out to our team today for a consultation. Let us help you make the transition to cleaner, more efficient driving.